“I’m depressed. What do I do?”
If you’ve typed that into Google or whispered it to yourself in the middle of the night, you’re not alone.
Maybe you’ve said things like:
- “I think I’m depressed, but I’m not sure.”
- “I’m so depressed I can’t do anything.”
- “Help me. I’m depressed and I don’t know what to do.”
Maybe you haven’t said anything at all, and you’re just trying to survive the day without breaking.
Whatever brought you here, hopelessness, exhaustion, numbness, or that heavy feeling that never quite goes away, I’m glad you landed on this page.
This article won’t throw fake positivity at you.
Let’s talk about what’s going on, why it’s not your fault, and what you can do next (even if you have zero energy to try).
You’re Depressed. Now What? (Start Here, Even If You’re Exhausted)
Let’s be real, when you’re depressed, even the idea of doing something about it can feel impossible. Getting out of bed is a battle. Texting someone back feels like too much. And advice like “just talk to someone” sounds laughable when you don’t even know what to say.
So here’s where we start: You don’t have to fix everything today.
You just need to do one small thing.
It could be this article. It could be drinking a glass of water. It could be writing down the sentence, “I’m not okay.” That counts.
Because depression tells you that nothing will help, and then uses your exhaustion as proof. But the fact that you’re here, reading this, means something in you still wants better. That’s your anchor.
If your mind is screaming, “I’m so depressed I can’t do anything”, do one thing. That’s all.
If you’re thinking, “I need help, I’m depressed,” but feel too ashamed to ask, read on. No judgment here.
You don’t need a full plan right now. You just need a lifeline, and that starts with knowing what you’re feeling is real, serious, and treatable.
How to Know If You’re Really Depressed (Or Just Burned Out)?
You’re tired all the time. You can’t focus. Everything feels heavy, and nothing feels worth it.
So is it depression, or are you just overwhelmed and drained?
Here’s the truth: burnout and depression can look almost identical on the outside, but the root cause and the way they affect you are different.
Signs It Might Be Depression:
- You wake up dreading the day, even after rest
- The things you used to love feel meaningless
- You feel hopeless, numb, or flat, even during “good” moments
- You cry out of nowhere, or not at all because you just feel empty
- You’ve lost interest in people, hobbies, food, sex, and life
- You think things like, “What’s the point?”, or “I don’t care anymore”
Signs It Might Be Burnout:
- You feel mentally exhausted, especially from work or responsibility
- You’re easily irritated, but not necessarily sad
- A vacation, break, or weekend helps a little
- You can still feel joy, just not often
- You’re overwhelmed by what you’re doing, not detached from who you are

If you’re thinking, “I’m always depressed, but I don’t know why”, you don’t need to have an answer to deserve help.
Burnout may go away with rest. Depression sticks around even when nothing’s wrong.
And if you’re unsure? That’s okay. A therapist can help you figure it out, you don’t have to diagnose yourself.
Silent Depression: When You’re Smiling But Numb
Some people cry every day. Others joke in meetings, take care of their families, and post smiling selfies.
Both might be deeply depressed.
Silent depression is when everything looks “fine” from the outside, but inside, you feel disconnected, hopeless, and exhausted.
You go to work. You reply to texts. You laugh at jokes. But it’s not real.
You’re not okay. You’re just on autopilot.
Signs You Might Be Masking Depression:
- You say “I’m fine” because it’s easier than explaining
- You overwork, over-help, or overcompensate to stay distracted
- You’re emotionally numb most of the time
- You collapse when you’re finally alone, because no one sees the real you
- You feel like a fraud for pretending everything’s okay
Silent depression is dangerous because it hides. And when no one sees your pain, you start to believe it doesn’t matter. But it does.
If you’re thinking, “I’m feeling depressed, but I can still function, so maybe I’m not really depressed,”
That’s exactly what depression wants you to believe.
You don’t have to hit rock bottom to ask for help. You don’t need anyone’s permission to start healing.
“I Don’t Know Why I’m Depressed,” and That’s Still Valid
Sometimes, there’s a clear trigger: a breakup, a loss, a trauma.
But a lot of people say, “I’m depressed and I don’t even know why.”
That doesn’t make it less real.
Depression isn’t always about what’s happening around you. Sometimes, it’s about what’s been building inside you for years, stress, unresolved emotions, hormone shifts, past pain, even genetics.
You might feel:
- Guilty for feeling low, “when you have a good life”
- Confused because “nothing bad happened”
- Frustrated that you can’t “snap out of it”
- Lost because it doesn’t make sense, even to you
You’re not making it up. You’re not attention-seeking.
And no, you don’t need a dramatic reason to deserve support.
If you feel like, “I’m depressed for no reason,”
The reason is simple: your brain and your body are struggling. That’s enough.
Let’s stop needing permission to take care of ourselves.
Why You Feel Worse When You’re Alone
You hold it together all day. You smile at people. You do what you’re supposed to.
But then you’re alone, and everything crashes.
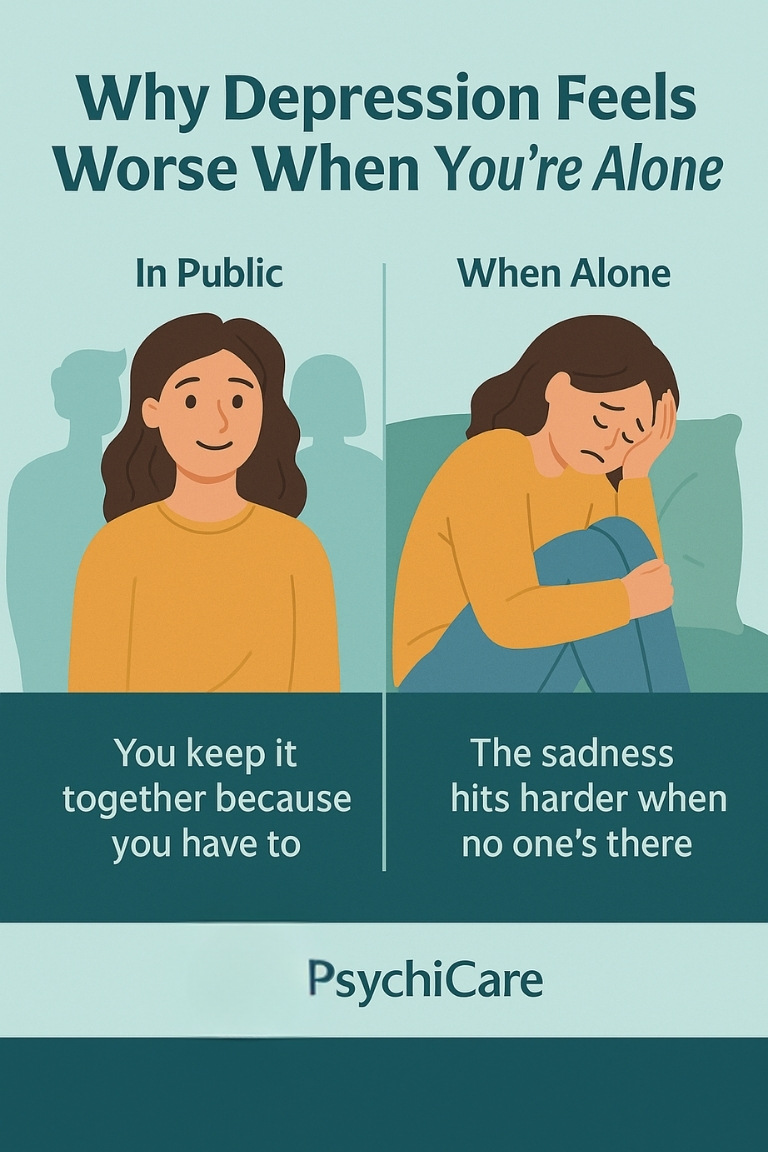
This is one of the most painful and common parts of depression.
Here’s why it hits harder in silence:
- You’re no longer distracted
- The thoughts get louder when no one’s around
- You finally feel safe to fall apart
- You don’t have to perform, so the truth shows up
- The loneliness feels bigger than your space can hold
Being alone with your depression doesn’t just feel empty; it can feel unbearable.
You might think: “I’m so depressed when I’m alone. I can’t do this.”
You might even dread weekends or evenings, not because you’re busy, but because you’re not.
And if you find yourself crying more, overthinking, or spiraling as soon as you’re alone,it doesn’t mean you’re weak. It means you’re hurting, and your body finally stops pretending when the world stops watching.
You’ve Tried to Snap Out of It, But It’s Not That Simple
You’ve told yourself to stop overthinking.
You’ve gone for walks. Tried to journal. Watched self-help videos.
Maybe you’ve even said, “I’m just being dramatic. I’ll be fine.”
But it’s still there.
Depression doesn’t go away because you want it to. It’s not about willpower. It’s not laziness. It’s not a lack of effort.
You might be thinking:
- “I’ve done everything right. Why do I still feel like this?”
- “I keep trying and failing, maybe this is just who I am.”
- “Nothing helps, so maybe nothing will.”
You’re exhausted, not just physically, but emotionally.
And the truth is: trying to fight depression alone often makes you feel worse when it doesn’t work.
But here’s what you need to hear:
If you’re thinking, “I’m depressed and I’ve tried everything,”
It doesn’t mean you’ve failed. It probably means you’ve been doing it alone too long.
I’m Too Depressed to Work, Move, or Think, What Can I Do?
Sometimes depression doesn’t just feel sad, it feels frozen.
You stare at your to-do list, your emails, your life… and nothing happens.
You’re not lazy. You’re completely overwhelmed.
You might say:
- “I’m so depressed I can’t get out of bed.”
- “I can’t think straight. I can’t function.”
- “I’m supposed to work, but I don’t even care.”
You’re not choosing this.
Your brain and body are slowing down to protect you from overload, from stress, from pain.
But it ends up trapping you instead.
If this is you, start here:
- Forget the big picture. Focus on one tiny thing.
- Sit up. Drink water. Breathe.
- Say, “I’m not okay, and that’s real.”
- Message one safe person. Even a one-word text.
- Let someone help you carry this.
If you’re thinking, “I’m too depressed to work,” or “I can’t even shower,”
Then surviving the day is enough. That’s not weakness. That’s fighting with everything you have.
If You’re Thinking “I Need Help”, Here’s Where to Start
If you’ve said it, even quietly, even just in your head, “I need help, I’m depressed”
That’s not weakness. That’s your strength showing up when you thought you didn’t have any left.
But let’s be honest: asking for help can feel impossible when depression is telling you you’re a burden, or it won’t work, or you don’t deserve it.
Here’s the truth: you do deserve help. You are not too far gone.
Not sure where to begin? Try this:
- Tell someone you trust: “I think I need help. I’m not okay.”
- See a therapist, online or in person. You don’t need to know what to say. Just start.
- Text a mental health support line if talking is too much.
- Write down what you’re feeling. Read it out loud to yourself. Let it be real.
- Visit a site like PsychiCare and just explore. No pressure to book. Just read.
If you’re Googling, “I need help, I’m depressed,” or “Help me, I’m depressed,”
That is the first step. And it counts.
Even if you feel numb. Even if you don’t believe this will work. Reaching out matters. It can save your life.
Depression Feels Permanent. It’s Not.
When you’re in it, depression feels like forever.
It convinces you this is who you are now. That the fog, the pain, the nothingness, it’s just how life will be from now on.
But that’s depression lying to you. Again.
It’s not permanent. It’s powerful, yes, but it’s treatable. People get better every day. Even the ones who swore they never would.
You might think:
- “I’ve felt this way for so long, nothing’s going to help now.”
- “This is just my personality. I’m always like this.”
- “If I were going to get better, I would’ve by now.”
But your brain is sick right now. That’s what depression is: a disruption in how your thoughts, emotions, and energy work.
And like any illness, it can be treated. You’re not destined to feel like this forever.
You’re not broken. You’re just stuck.
And stuck isn’t the end. It’s just the place before something shifts.
What Help Looks Like (Therapy, Support, and First Steps)
- Therapy helps you untangle the mess. You don’t need the right words, just show up.
- You can talk to a professional online. No travel, no pressure. Just real support.
- Medication helps some people. It’s not a last resort, it’s a valid tool.
- Support groups remind you you’re not alone. Hearing “me too” changes things.
- The first step isn’t fixing everything. It’s asking for help once. That’s enough to start.
You don’t have to figure it all out. You just have to take one honest step.
FAQs About Depression and What to Do
What should I do if I’m feeling very depressed?
Start small. Tell someone. Book one therapy session. Drink water. Breathe. You don’t need to fix everything, just take one step.
I think I’m depressed. What should I do?
If you’re thinking it, trust it. You don’t need proof or a diagnosis to ask for help. Therapy is a great first step.
I’m so depressed I can’t work, what now?
That’s not laziness, it’s overwhelm. If your body shuts down, listen. Mental health breaks are valid. Talk to a doctor or therapist.
What if I’m depressed for no reason?
You don’t need a “why” to be struggling. Depression can happen even when life seems okay. It’s still real, and it’s still treatable.
Is depression curable?
It’s treatable. Many people recover fully, and others learn how to manage it. Either way, you don’t have to stay stuck.




